At a Glance
- Direct frequency modulation at 1550 nm and coherent detection enable longer range, intrinsic amplification and glare suppression
- High resolution (sub-cm) at long range
- High sensitivity (signal < 1nW detectable)
- Effective DSP and mirror control
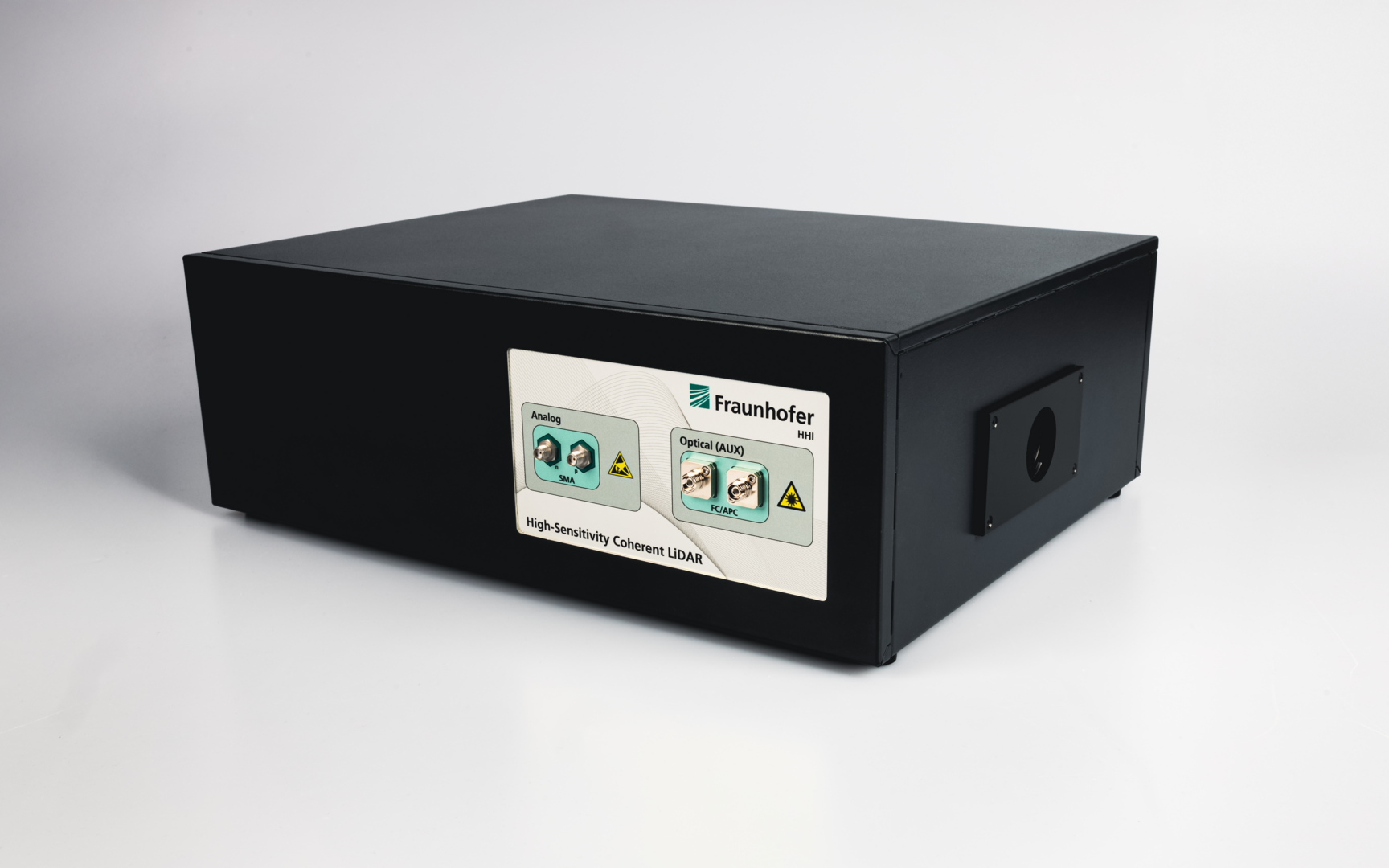
- All fiber-based optics
- Reduced system complexity by monostatic design using 2D mirror scan
Technical Background
The Fraunhofer Institute HHI demonstrates a real-time LiDAR prototype for robotics and automation applications using a fiber-based design with FMCW detection and 2D mirror scanning. Its high resolution (sub-cm) and long range (>200m) show our latest advancements in high-sensitivity coherent detection and signal processing technology.
Features
- Scalability by using standard communication components
- Quasi-solid-state solutions for scanning
- Fiber-based optical frontend
- Real-time pointcloud by FPGA
- Effective DSP and mirror control for high resolution
- High sensitivity receiver for long range at low reflectance
- Eye-safe operation
Applications
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 3D Imaging
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Smart Infrastructure & Logistics
- Robotics and Automation
- Industry 4.0
| Parameter | Version A | Version B | Version C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanning Mechanism | Galvo Mirror | Galvo Mirror | MEMS Mirror |
| Frequency Modulation | External Mod. | Direct Mod. | Direct Mod. |
| Resolution (°) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Range (10% target) (m) | > 200 | ~ 200 | ~ 20 |
| Horizontal Field of View (°) | 40 | 40 | ~ 8 |
| Vertical Field of View (°) | 40 | 40 | ~ 8 |
| Distance Precision (1σ spread) | 0.0005% | 0.1% | 0.2% |
| Accuracy (cm) | < 0.5 | 1–3 | 5 |
| Framerate (Hz) | 0.1 | 0.1v | > 0.1 - 1 |
| Standoff (cm) | 10 | 10 | 5 |
| Application | ADAS Industry 4.0 | Robotics Industry 4.0 | ADAS Monitoring Robotics |

